|
|
| Breast Cancer |
 |
 |
|
|
|
|
|
Breast cancer is a feared disease. Even though lung cancer and heart disease
kill more women each year, surveys show that women view breast cancer as the
biggest threat to their health.
But women can take steps to lower their risk.
To access your Bladder Cancer Risk completely, at ScienceofLife we have
produced a general questionnaire with a fair knowledge of risk Factors and
related knowledge base.
|
|
|
|
|
Questionnaire :
To estimate your risk of breast cancer, take about 2 to 3 minutes to answer
some questions about your health, lifestyle and personal background.
Please fill in these questions to access your risk of Breast Cancer.
|
| 1. What is your sex?
Please enter your sex |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Risk Factors:
Most scientists agree that these things affect the risk of breast
cancer. Some may apply to you, but others may not.
Age and breast cancer :
The risk of developing breast cancer increases with age. Rates are generally
low in women under 40, start to increase after 40, and are highest in those 70
and older. The average age breast cancer is found is 62.
Back to Risk Factors
Sex and breast cancer :
Though breast cancer can develop in men, over 99 percent of all cases in the
United States are diagnosed in women.
Back to Risk Factors
Height and breast cancer :
Tall women have a higher risk of breast cancer. Scientists aren't sure why. One
reason may be that tall people have more cells in their bodies, which increases
the number of cells that could become cancerous. Another reason may be that
tall people grow faster as children. Faster growth is linked to changes in the
genetic structure (DNA) of the body's cells, eventually causing them to become
cancerous. Tall women also have a higher risk of colon cancer and tall men have
a higher risk of colon cancer as well.
Back to Risk Factors
Weight and breast cancer :
Women who maintain a healthy weight have a lower risk of breast cancer,
especially if they are post-menopausal. This is because losing weight lowers
the level of estrogen in a woman's body. Estrogen is a female reproductive
hormone that is released during the menstrual cycle in premenopausal women but
also released by fat cells after menopause. High levels of estrogen after
menopause may cause cells in the breast to become cancerous. People who
maintain a healthy weight also have a lower risk of colon cancer, kidney
cancer, heart disease, diabetes and stroke. And women have a lower risk of
uterine cancer.
Back to Risk Factors
Vegetables and breast cancer :
Women who eat at least 3 servings of vegetables a day have a lower risk of
breast cancer. Vegetables contain the antioxidant vitamin A. Low levels of
vitamin A are linked to breast cancer. 1 serving of vegetables is:
-
1 cup of raw leafy greens like lettuce or spinach
-
½ cup of other vegetables, raw or cooked
-
½ cup of cooked beans or peas
People who eat vegetables also have a lower risk of colon cancer, lung
cancer,diabetes and stroke.
Back to Risk Factors
Alcohol and breast cancer :
Women who have less than one drink a day have a lower risk of
breast cancer. Alcohol may raise the level of estrogen in a woman's body.
Estrogen is a female reproductive hormone mainly released during the menstrual
cycle. High levels of estrogen after menopause may cause cells in the breast to
become cancerous. A drink is a can of beer, a glass of wine, or a shot of hard
liquor.> People who limit alcohol also have a lower risk of colon cancer,
high blood pressure, and stroke. But drinking moderate amounts has benefits
too. People who drink moderate amounts have a lower risk of heart disease and
diabetes.
Back to Risk Factors
Age at first period and breast cancer :
Women who get their first period at an early age have a higher risk of breast
cancer. This is because an early period exposes a woman's body to greater
amounts of estrogen over her lifetime. Estrogen is a female reproductive
hormone mainly released during the menstrual cycle. High levels of estrogen can
cause cells in the breast to become cancerous.
Back to Risk Factors
Age at first birth and breast cancer :
Women who give birth to their first child at a late age have a higher risk of
breast cancer. One reason may be that pregnancy appears to permanently change
breast tissue, making it less likely to become cancerous. The later this change
occurs after a woman has her first period, the more time breast cells have to
become cancerous.
Back to Risk Factors
Age at menopause and breast cancer :
Women who go through menopause (when regular periods stop) at a later age than
usual have a higher risk of breast cancer. This is because a late menopause
exposes a woman's body to greater amounts of estrogen over her lifetime.
Estrogen is a female reproductive hormone mainly released during the menstrual
cycle, which can cause cells in the breast to become cancerous. Women who go
through late menopause also have a higher risk of uterine cancer.
Back to Risk Factors
Number of births and breast cancer :
Women who have less than 2 children have a higher risk of breast cancer. This
is because pregnancy changes breast tissue in a way that prevents breast cells
from becoming cancerous. The fewer pregnancies a woman has, the less her breast
tissue changes. Women who have less than 2 children also have a higher risk of
ovarian cancer. But women who have 2 or more children have a higher risk of
cervical cancer.
Back to Risk Factors
Breast feeding and breast cancer :
Women who breast feed for at least one year combined over all
pregnancies have a lower risk of breast cancer. This is because breast feeding
changes the tissue in a woman's breasts. This change helps prevent breast cells
from becoming cancerous. Women who breast feed also have a lower risk of ovarian
cancer.
Back to Risk Factors
Birth control pills and breast cancer :
Women have a higher risk of breast cancer while they are taking birth control
pills. The link between birth control pills and breast cancer is shown in many
studies, but scientists don't know why. Birth control pills can have positive
and negative effects on a woman's health. If taken for at least 5 years, birth
control pills can lower a woman's risk of colon cancer, uterine cancer and
ovarian cancer. But while she's taking them, they raise her risk of breast
cancer, heart attack and stroke. For some women, they can also cause side
effects like nausea and vomiting.
WARNING : Smoking and taking birth control pills can be a
deadly combination. Together, they greatly increase the risk of a heart attack
and stroke. All women who smoke should quit for good as soon as possible.
Back to Risk Factors
Post-menopausal hormones and breast
cancer
:
Post-menopausal hormones are medications that help ease the symptoms of
menopause, like hot flashes and vaginal dryness. They contain hormones that are
similar to the female reproductive hormones estrogen and progesterone, which
the body stops making in large quantities after menopause. Women who take
post-menopausal hormones for 5 or more years have a higher risk of breast
cancer. This is because post-menopausal hormones raise the level of estrogen in
a woman's body. Estrogen is a female reproductive hormone mainly released
during the menstrual cycle. High levels of estrogen after menopause may cause
cells in the breast to become cancerous. Post-menopausal hormones can have
positive and negative effects on a woman's health. They can lower a woman's
risk of colon cancer and osteoporosis (bone loss). But they can raise her risk
of breast and uterine cancer. And, although post-menopausal hormones were once
thought to lower the risk of heart disease, it is now unclear exactly how they
affect the risk of the disease.
Back to Risk Factors
Benign breast disease and
breast cancer :
Benign breast disease is a large group of non-cancerous conditions of
the breast that includes cysts, fibroadenomas, and hyperplasia. Of all the
types of benign breast disease, only hyperplasia is related to breast cancer.
There are two types of hyperplasia: intraductal hyperplasia and atypical
hyperplasia. Intraductal hyperplasia takes place when extra cells grow along
the ducts of the breast. Atypical hyperplasia takes place if these cells become
abnormal. Women who have hyperplasia have a higher risk of breast cancer. This
is because the extra cells within the ducts can become increasingly abnormal.
But in general, hyperplasia rarely becomes cancer.
Back to Risk Factors
Family history and breast cancer Women
who have a mother or sister with breast cancer have a higher risk of the
disease, especially if they were diagnosed at a young age. And the risk goes up
if a woman has a mother and sister with the disease. This is because a small
number of breast cancers are linked to mutations in the genetic structure (DNA)
of your body's cells. These mutations can be passed on from generation to
generation. With many diseases, people who have a family history have a higher
risk. A family history raises the risk of several cancers like bladder,
ovarian, kidney and skin cancer. It also raises risk of heart disease,
diabetes, bone loss> (osteoporosis) and stroke.
Back to Risk Factors
Jewish ethnicity and breast cancer :
Jewish women have a higher risk of breast cancer, especially women of Ashkenazi
descent. This is because they are more likely to have genetic mutations linked
to breast cancer risk. Genetic mutations are inherited changes in the genetic
structure (DNA) of the body's cells. They can be passed on from generation to
generation.
Back to Risk Factors
|
| Fact Analysis
|
|
What is breast cancer?
Breast cancer occurs when cells in the breast grow out of control. The cells
clump together and form a malignant (cancerous) tumor.
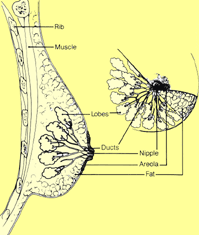
Each breast has several sections called lobes. Each lobe has smaller sections
called lobules, which produce milk when a woman is breast feeding. The lobes
and lobules are linked by tubes called ducts. Ducts are the tubes that carry
the milk from the lobules to the nipple. The rest of the breast is mostly made
up of fat.
There are two main types of breast cancer. Breast cancer that begins in the
lobes and spreads to nearby tissue is called invasive lobular carcinoma. Breast
cancer that begins in the ducts and spreads to nearby tissue is called invasive
ductal carcinoma.
|
|
|
|
There is also a condition called carcinoma in situ, where there are abnormal
cells in the breast, but they are not cancerous. Still, carcinoma in situ is a
sign that breast cancer may develop at a later time. Lobular carcinoma in situ
(LCIS) are abnormal cells that originate in the lobules. Ductal carcinoma in
situ (DCIS) are abnormal cells that originate in the ducts.
Most breast tumors are benign, which means they are not cancerous. Benign
breast tumors are not life threatening and do not spread outside the breast.
Back to Fact Analysis
How common is breast cancer?
Breast cancer is the most common cancer among women in the US, and it's more
common among older women. About 180,000 American women are diagnosed with the
disease each year. Breast cancer also affects a small number of men in the US.
About 1,600 American men are diagnosed with the disease each year.
Back to Fact Analysis
Who is at risk of getting breast cancer?
Anyone can get breast cancer (including men), but it usually strikes women over
age 50. And the risk quickly goes up with age. Women who have a family history
of breast cancer have a higher risk.
Back to Fact Analysis
How do you lower your risk of breast cancer?
-
Cut down on the amount of alcohol you drink.
-
Maintain a healthy weight.
-
Eat more vegetables.
A drug called tamoxifen Back to fact sheetmay also lower the risk of
breast cancer, but only for women who are at high risk of the disease.
Researchers are still studying its long-term effects.
Back to Fact Analysis
Who should get breast cancer screening tests?
Back to fact sheetAll women over the age of 20 should get screened regularly
for breast cancer. But the right screening tests mainly depend on a woman's
age. Use this chart to find out which tests you should get.
|
|
If you are between ages 20 and 39
|
Get a clinical breast exam every 1 - 3 years.
|
|
If you are between ages 40 and 49
|
Get a clinical breast exam every year.
Women at high risk of breast cancer may need to have regular mammograms. Talk to
your doctor.
|
|
If you are age 50 or older
|
Get a mammogram and clinical breast exam every year.
|
|
|
Be sure to discuss your risk of breast cancer with a doctor. If your risk is
high, you may need to have mammograms more often and at an earlier age.
Back to Fact Analysis
What are the symptoms of breast cancer?
Back to fact sheetBreast cancer may have no symptoms in the
early stages. But as the cancer grows, the symptoms may include:
-
A lump or mass in the breast or the under arm area
-
A change in breast size, shape or color
-
A discharge from the nipple
-
A change in the feel of the skin covering the breast (the skin could become
dimpled, puckered or scaly)
Some of these symptoms may be caused by other problems. Only a doctor can know
for sure. If you have any of these symptoms, talk to a doctor immediately.
Back to Fact Analysis
|
|
|
|
 |
 Major
Topics Major
Topics |
 |
|
|
|
 |
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|