|
|
| Lung Cancer
|
 |
 |
|
|
Lung cancer is the #1 cancer killer in the US. But the good news is that it
doesn't have to be. 90% of all lung cancers could be prevented if everyone quit
smoking.
To access your Lung Cancer Risk completely, at ScienceofLife we have produced a
general questionnaire with a fair knowledge of risk Factors and related
knowlegebase.
|
|
|
|
|
Questionnaire :
To estimate your risk of lung cancer, take about 2 to 3 minutes to answer some
questions about your health, lifestyle and personal background.
Please fill in these questions to access your risk of Lung Cancer.
|
| 1. What is your sex?
* |
|
|
| 2.
What is your age?
Please enter your age
Please enter Valid Age |
|
Years |
| 3. Have you ever had any type
of cancer (except for non-melanoma skin cancer)?
* |
|
|
| 4. Do you eat 3 or more
servings of vegetables a day? 1 serving is about 1 cup of raw leafy greens or ½
cup of other vegetables, raw or cooked.
* |
|
|
| 5. Do you eat 3 or more
servings of fruit a day? 1 serving is about ½ a grapefruit or ½ a large banana.
* |
|
|
| 6. Do you smoke
cigarettes? |
|
|
| 7. Have you smoked one or
more cigars a day for the past year?
* |
|
|
| 8. Have you lived in or near
a large city for at least 10 years of your life?
* |
|
|
| 9. Have you ever worked with
asbestos?
* |
|
|
| 10. Have you ever worked with
any of these chemicals? Radon, Cadmium, Chromium, Beryllium, Aluminum, Silica,
Sulfuric acid mist, Bis(chloromethyl) ether and chloromethyl ether Coke Mustard
gas
* |
|
|
| 11. Have you ever been
involved with any of the following processes?
Arsenic smelting, Coal gassification, Iron or steel founding
* |
|
|
| 12. Has your brother, sister
or parent ever had lung cancer?
* |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Back to top
|
|
|
Risk factors :
Most scientists agree that these things affect the risk of lung
cancer. Some may apply to you, but others may not.
Age and lung cancer :
The risk of lung cancer goes up with age. Rates of the disease are low in
people under 40; they then increase significantly from age 40 until after 75.
Back to Risk Factors
Vegetables and lung cancer :
People who eat at least 3 servings of vegetables a day have a lower risk of
lung cancer. Vegetables contain cancer-fighting antioxidant vitamins, like
vitamins A and C.
1 serving of vegetables is:
-
1 cup of raw leafy greens like lettuce or spinach
-
1/2 cup of other vegetables, raw or cooked
-
1/2 cup of cooked beans or peas
People who eat vegetables also have a lower risk of colon cancer, diabetes and
stroke. And women who eat vegetables have a lower risk of breast cancer.
Back to Risk Factors
Fruits and lung cancer :
People who eat at least 3 servings of fruit a day have a lower risk of lung
cancer. Fruits contain cancer-fighting antioxidant vitamins, like vitamins A
and C.
1 serving of fruit is:
-
1 medium-sized piece of fruit or 1/2 cup of small or cut-up fruit
-
1/3 cup of 100% fruit juice
-
1/4 cup of dried fruit
People who eat fruit also have a lower risk of stomach cancer, heart disease,
diabetes and stroke.
Back to Risk Factors
Smoking cigarettes and lung cancer :
People who smoke cigarettes have a much higher risk of lung cancer. In
fact, 90% of lung cancer occurs in people who smoke. Cigarette smoke contains
chemicals that damage the genetic structure (DNA) of the body's cells. DNA
damage causes cells to become cancerous. It doesn't matter how much a person
smokes. Even if someone smokes one cigarette a day, she still has a higher risk
of lung cancer than a non-smoker. The more a person smokes, the higher the
risk. Soon after quitting, the risk begins to drop. People who smoke cigarettes
also have a higher risk of cancers of the bladder, kidney, pancreas, lip,
mouth, tongue, larynx, throat and esophagus. Women who smoke have a higher risk
of cervical cancer. People who smoke even have a higher risk of other diseases
like diabetes, bone loss (osteoporosis), emphysema, and bronchitis!
Back to Risk Factors
Smoking cigars and lung cancer :
People who smoke cigars have a higher risk of lung cancer. Like cigarette
smoke, cigar smoke contains chemicals that damage the genetic structure (DNA)
of the body's cells. DNA damage can cause cells to become cancerous. The more a
person smokes and inhales, the higher the risk. Soon after quitting, the risk
begins to drop. People who smoke cigars (even if they don't inhale) also have a
higher risk of cancers of the voice box, esophagus and oral area (lip, mouth,
tongue and throat). And they have a higher risk of heart disease and stroke.
Back to Risk Factors
Second-hand smoke and lung cancer :
People who are able to avoid secondhand smoke have a lower risk of lung cancer.
Secondhand smoke contains chemicals that damage the genetic structure (DNA) of
your body's cells. DNA damage causes cells to become cancerous.
Back to Risk Factors
Air pollution and lung cancer :
People who live in a city for 10 or more years have a slightly higher risk of
lung cancer. Pollutants in the air -- like car exhaust and factory emissions --
are probably the cause.
Back to Risk Factors
Workplace chemicals and lung cancer :
People who are exposed to certain workplace chemicals have a higher risk of
lung cancer. This is because some chemicals can damage the genetic structure
(DNA) in the body's cells. DNA damage causes cells to become cancerous.
Workplace chemicals linked to lung cancer include asbestos, radon and chromium.
Processes like arsenic smelting are also linked to lung cancer. WARNING: If you
are a smoker, some chemicals like asbestos can mix with the smoke you inhale
and massively raise your risk of lung cancer.
Back to Risk Factors
Family history and lung cancer :
People who have a mother, father, brother or sister with lung cancer have a
higher risk of the disease. This is because some lung cancer is linked to
mutations in the genetic structure (DNA) of the body's cells. These mutations
can be passed on from generation to generation. With many diseases, people who
have a family history have a higher risk. A family history raises the risk of
several cancers like breast, bladder, kidney, stomach, skin cancer. It also
raises risk of diabetes, bone loss (osteoporosis) and stroke.
Back to Risk Factors
|
|
|
|
Fact Analysis
What is lung
cancer?
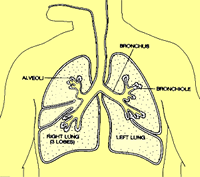
Lung cancer occurs when cells in the airways to the lungs grow out of
control. The cells clump together and form a malignant (cancerous) tumor. The
lungs are sponge-like organs that bring air in and out of the body through the
trachea. The trachea divides into tubes called bronchi, which divide into
bronchioles. Lung cancer usually starts in the lining of the bronchi.
Back to Fact Analysis
How common is lung cancer?
Lung cancer is the second most common cancer among men and women in the US, and
it's more common among older men and women. It's also the leading killer. About
160,000 Americans die of lung cancer each year. To compare this with other
cancers.
|
|
Back to Fact Analysis
Who is at risk of getting lung cancer?
Anyone can get lung cancer, but it usually strikes smokers over age
50. And the risk goes up with age. 90% of lung cancers occur in people who
smoke.
Back to Fact Analysis
How do you prevent lung cancer?
The single best way to prevent lung cancer is not to smoke. If you smoke, quit
for good as soon as possible. Not long after you quit, your risk of lung cancer
begins to drop. After 10 years of not smoking, the risk of lung cancer is about
50% lower compared to continued smokers and continues to decrease with time.
In addition to not smoking:
-
Eat more fruits and vegetables
-
Avoid second-hand smoke (smoke from other people's cigarettes and cigars)
-
Avoid exposure to chemicals (like asbestos) that can cause lung cancer
Back to Fact Analysis
What is the screening test?
There is no good screening test for lung cancer.
Back to Fact Analysis
What are the symptoms of lung cancer?
Lung cancer often does not cause symptoms for many years. But as the cancer
grows, symptoms may include:
-
persistent cough
-
Chest pain
-
Hoarseness
-
Weight loss and loss of appetite
-
Spit or phlegm that is bloody or rust-colored
-
Shortness of breath
-
Repeated bouts of pneumonia or bronchitis
These symptoms may also be caused by something less serious like an infection.
Only a doctor can know for sure. If you have any of these symptoms, talk to a
doctor immediately.
Back to Fact Analysis
|
|
|
|
 |
 Major
Topics Major
Topics |
 |
|
|
|
 |
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|