|
|
Hi Guest!
Font 
 |
Home > Risks > Melanoma Detail |
|
|
|
|
| Melanoma Cancer
|
 |
 |
|
|
Melanoma is a type of skin cancer. It's the least common but also the most
dangerous. Like all types of skin cancer, it's easy to prevent. Protect your
skin from the sun. And be sure to help kids protect their skin. Getting bad
sunburns as a child is the leading risk factor for melanoma.
To access your Melanoma Cancer Risk completely, at ScienceofLife we have
produced a general questionnaire with a fair knowledge of risk Factors and
related knowlegebase.
|
|
|
|
|
Risk factors :
Most scientists agree that these things affect the risk of melanoma.
Some may apply to you, but others may not.
Age and melanoma :
The risk of melanoma goes up with age, yet it tends to develop earlier
in life than many other cancers. The average age at diagnosis is 57.
Back to Risk Factors
Physical features and melanoma :
People who have light-colored hair, light-colored eyes, or fair skin
have a higher risk of melanoma. This is because people with these features
often have low levels of pigment in their skin and are more likely to get
sunburned. Pigment gives skin its color. High levels of pigment make skin
darker and help protect it from the sun. Sunlight can cause skin cells to
become cancerous.
Back to Risk Factors
Sunburns and melanoma :
People who have severe, repeated sunburns as children have a higher risk of
melanoma. This is because sunburns in childhood can cause skin cells to become
cancerous later in life. Sunburns as an adult also raise the risk of skin
cancer.
Back to Risk Factors
Immunosuppressive drugs and melanoma :People who've taken immunosuppressive drugs have a higher risk of
melanoma. After an organ transplant, these drugs prevent the body from
rejecting the new organ. But they also prevent the body from responding to cell
growth. This means that when a person is taking them, their skin cells can grow
out of control and become cancerous.
Back to Risk Factors
Family history and melanoma :
People who have a mother, father, brother, or sister with melanoma have a
higher risk of the disease. This is because some cases of melanoma are linked
to mutations in the genetic structure (DNA) of the body's cells. These
mutations can be passed on from generation to generation. With many diseases,
people who have a family history have a higher risk. A family history raises
the risk of several cancers like lung, breast, prostate, colon, bladder,
uterine, ovarian, kidney, stomach, pancreatic and other types of skin cancer.
It also raises the risk of diabetes, bone loss (osteoporosis) and stroke.
Back to Risk Factors
|
|
|
Fact Analysis
|
 |
|
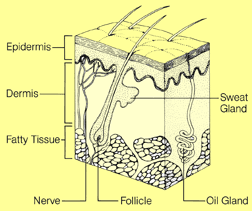
What is melanoma?
Melanoma is a type of skin cancer. It's the least common but also the most
dangerous. It begins in skin cells called melanocytes. Melanocytes grow in
groups and form moles. Most moles are not cancerous. But when melanocytes grow
out of control, they become melanoma. Melanoma accounts for 4% of all skin
cancer. The other types of skin cancer are called basal cell cancer and
squamous cell cancer. They are less dangerous than melanoma because they are
highly curable. The skin is the body's biggest organ. It protects us against
sunlight, injury and infection. It also regulates body temperature. It has 2
main layers: the outer layer (epidermis) and the inner layer (dermis).
Back to Fact Analysis
How common is melanoma?
About 47,000 Americans are diagnosed with melanoma each year. About 1.3 million
Americans are diagnosed with other types of less serious skin cancer.
Back to Fact Analysis
Who is at risk of getting melanoma?
Anyone can get melanoma. The risk usually goes up with age. And people with
light-colored hair, eyes and skin have a higher risk than people with darker
coloring. People with a family history of melanoma also have a higher risk.
Back to Fact Analysis
How do you prevent melanoma?
-
Protect your skin from the sun.
-
Be sure to protect the kids in your life as well.
Kids need extra protection from the sun because their skin is more likely to
burn. Be an example for them to follow.
Back to Fact Analysis
What is the screening test?
There is no good screening test for melanoma. But you can check your skin for
signs of an unusual mole or changes in a mole you've had for a long time. If
you're concerned about melanoma, talk to a doctor about your risk.
Back to Fact Analysis
What are the symptoms of skin cancer?
The main symptom of melanoma is an unusual mole. Signs of an unusual mole are:
-
It changes in size, shape, or color
-
Half of the mole does not look like the other half
-
The edges of the mole are uneven, ragged, or notched
-
The mole is not evenly colored.
-
The mole has different shades of tan, brown, or black and may have patches of
red, blue, or white
-
The mole is wider than a quarter of an inch – about the width of a pencil
eraser
Most moles are normal and harmless. A normal mole is usually an evenly colored
black, tan, or brown spot that does not change size or shape. If you have an
unusual mole or notice a change in a mole you've had for a long time, see a
doctor immediately.
Back to Fact Analysis
|
|
|
|
|
 |
 Major
Topics Major
Topics |
 |
|
|
|
 |
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Please Rate This Page: How useful is this information for
you?
|
|
|
All material on this website is protected by International Copyright
Law © 1999-2026 by scienceoflife.com, Life Science Medical Center.
Best viewed in IE5.0+ (1024X768) resolution.
scienceoflife.com - Window To The Future of Medicine™
|
|